Electricity is so basic to the world economy that certain electricity indices are used to express a country’s economic standing (consumption or production of electricity per capita) and the standard of living enjoyed by a people (per capita electricity consumption in the domestic sector). Moreover, electricity supply has special characteristics which make the service unique as compared to other types of industry. The end product has to be delivered instantaneously and automatically upon the consumer’s demand; except for pumped storage plants and Electric batteries, technologies do not exist that can produce it economically at uniform rates, hold it in storage in large quantities, and deliver it under convenient schedules; insufficient capacity (shortage) or excessive capacity (idle capacity)
have negative effects on the economy; the close inter-relation with economic and social factors imposes labour, environmental, financial and other constraints on the problem. Careful Planning of the Electric sector is therefore of great importance since the decisions to be taken involve the commitment of large resources, with potentially serious economic risks for the electrical utility and the economy as a whole
Power system Planning is part of a more general problem, that of energy and economic development planning. Its objective is therefore to determine a minimum cost strategy for long-range expansion of the generation, transmission and distribution Systems adequate to supply the load forecast within a set of technical, economic and political constraints. Traditionally, Power system Planning has been mainly related to generation expansion planning. This is due mainly to the fact that investment in transmission lines is a relatively small fraction of the investment in the construction of Power stations and that investment in the distribution of Electric energy to customers, although sizeable, is to a large extent independent of the generation and transmission system.
The main steps in Power system Planning may be summarized as follows:
(a) Study of the Electric load forecast 5 to 30 years into the future, based on the most reliable information
Evaluation of the energy resources available in the future for electricity generation
and the foreseeable trends in technical and economic developments.
(c) Evaluation of the economic and technical characteristics of the existing system of generating units and of the plants that are considered as potential units for system expansion. These characteristics include capital investment cost, fuel cost,operation and maintenance costs, efficiencies, construction times, etc.
(d) Determination of technical and cost characteristics of the plants available for
expansion.
(e) Determination of the economic and technical parameters affecting decisions such as discount rate, level or reliability required from the generating system, etc.
(f) Choice of a procedure to determine the optimal expansion strategy within the
imposed constraints.
(g) Qualitative review of the results to estimate the viability of the proposed solution




















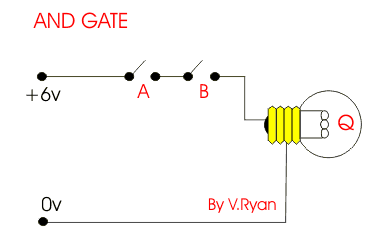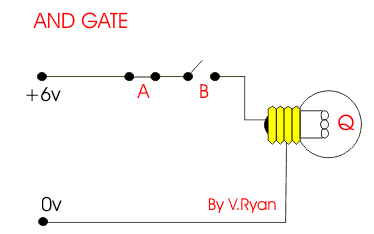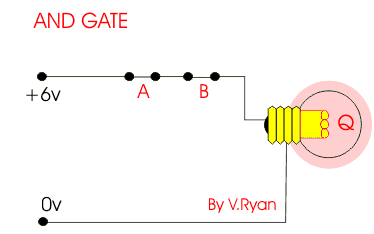
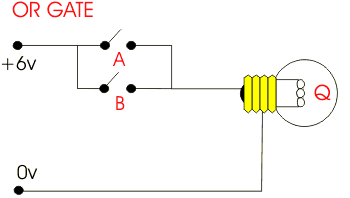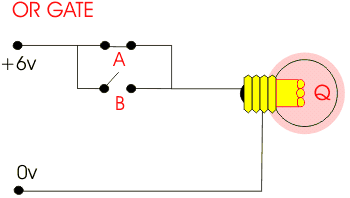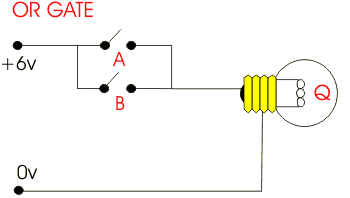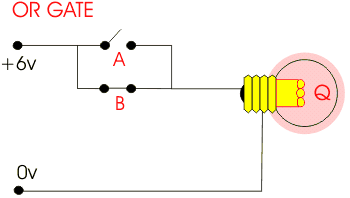
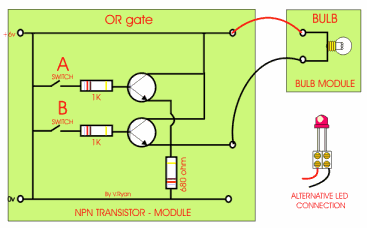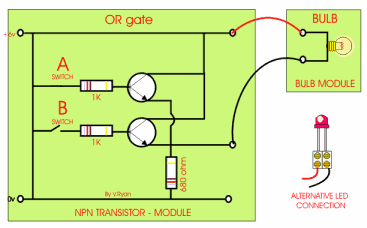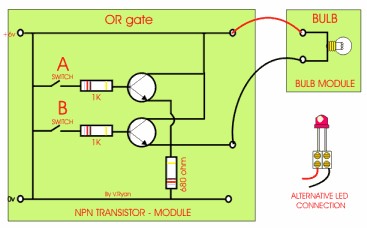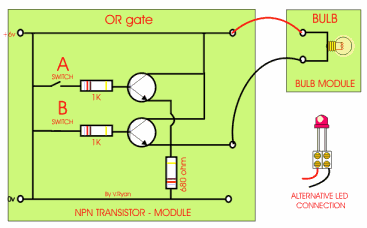
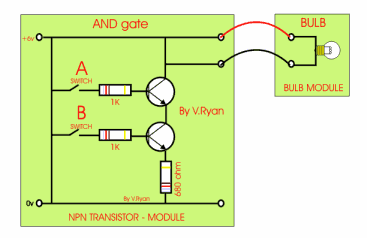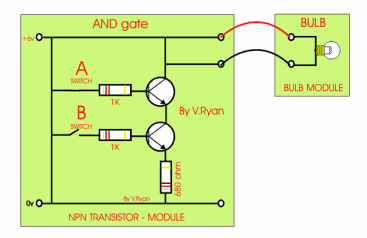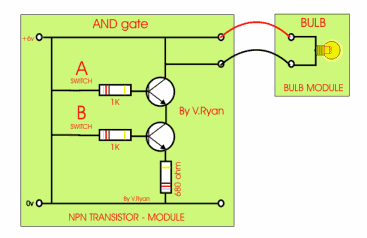 This is an AND gate circuit and it can be made quite easily. The example shown is built from a modular electronics kit. Both switches ‘A’ and ‘B’ must be pressed together for the bulb to light.
This is an AND gate circuit and it can be made quite easily. The example shown is built from a modular electronics kit. Both switches ‘A’ and ‘B’ must be pressed together for the bulb to light.